Please read the About page for important background information on this site.
 |
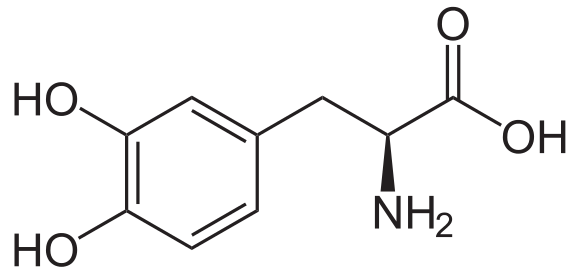 |
 |
The physiological basis of Parkinson’s (including known causes) |
Current and future therapeutics for Parkinson’s |
Other therapeutic options |
Recent drug approvals for Parkinson’s disease:
- 2019 and 2020: Three FDA approvals for add-on drugs that lessen “off” time: Ongentys (opicapone), a new COMT inhibitor; Nourianz (istradefylline), a first-in-class “adenonsine A2A antagonist”; and Inbrija (inhaled levodopa) for rescue dosing
- 2018: Xeomin (incobotulinumtoxinA), an injectable drug similar to Botox, for excessive drooling, a frequent symptom of Parkinson’s disease
- 2017 and 2018: Two new extended-release formulations of amantadine, Gocovri to treat levodopa-induced dyskinesias, and Osmolex ER for Parkinson’s symptoms.
- 2017: Safinamide (Xadago), for symptomatic benefit
- 2016: Pimavanserin (Nuplazid), for hallucinations and delusions associated with Parkinson’s disease psychosis
- 2015: Rytary, a new extended-release formulation of levodopa/carbidopa (the same drugs in Sinemet), discussed briefly on the levodopa pharmacokinetics page
- 2015: Duopa, levodopa/carbidopa delivered directly into the small intestine, to reduce off time and dyskinesias, also discussed briefly on the levodopa pharmacokinetics page
- 2014: Droxidopa (Northera), for orthostatic hypotension (low blood pressure, especially upon standing up)
Additional reliable information on these recently approved drugs available on the Michael J. Fox Foundation website.
I was recently hosted by PDActive to give a talk called “Hope and Reality on the Path to Curing Parkinson’s Disease” which they have kindly posted on Youtube.